Which MRI is better with or without contrast? Contraindications to the use of MRI contrast agents. Contrast agents for MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the most reliable ways to diagnose the body. But in some cases, a standard study may not be enough. The examination must be carried out using a special contrast agent, which allows identifying a number of pathologies at an early stage.
How does contrast agent work?
Typically, a contrast agent for MRI is used in controversial situations when it is necessary to clarify the results of previous studies. It plays the role of a kind of indicator of changes in the body. Using contrast, you can not only determine the location of the tumor, but also its size and structure.
Once in the body, the contrast moves through the vessels and into large quantities accumulates precisely in the area of the neoplasm, emphasizing its boundaries on MRI. Thanks to such research, inflammatory processes and degenerative changes are determined.
MRI of the brain with contrast allows for detailed visualization and study of tumors
Certain substances are used for the procedure:
- Gadovist,
- Magnevist,
- Omniscan,
- Let's do it.
All drugs contain gadolinium salts. This soft metal, having a silvery tint. It dissolves well, and after the procedure is excreted from the body along with urine. Salts have no side effects, but are extremely toxic and sometimes cause an allergic reaction.
Another advantage of using a contrast agent is that it allows you to distinguish benign tumor from malignant. To do this, specialists monitor the accumulation of salts and the intensity of the signal from problem tissues. Thus, benign neoplasms accumulate substances slightly, while malignant ones are emphasized many times more clearly.
Indications and contraindications
MRI using a contrast agent is indicated for patients with vascular diseases or various tumors. The list of indications includes:
- spinal or brain tumor;
- prostate tumors (before and after operations);
- aneurysm;
- brain injuries;
- metastases;
- period after removal of a herniated disc.
This study is also used for overdiagnosis in cases of complaints of pain in the testicles, prostate gland or mammary glands. The substance is also necessary when examining the brain for diseases of the central nervous system, meningitis or Alzheimer's disease.
In some cases, testing with salts is not recommended or it is advisable to postpone it. Thus, contrast should not be administered to patients with liver or kidney failure. It is not recommended to undergo MRI during pregnancy, if you have electronic or metal implants, are overweight, or have severe somatic pathologies. If the patient is claustrophobic, only open tomography machines can be used.

Before administering a contrast agent, make sure that the patient is not allergic to it.
During lactation, contrast is relatively safe. The study can be carried out, but breastfeeding must be excluded for a day. Substances enter milk in small doses, but this may be enough to cause an allergic reaction in a child.
Adverse reactions following the administration of contrast agents are rare. These include:
- nausea,
- dizziness,
- vomit,
- headache.
All alarming symptoms disappear within 2-3 hours after the study. After the procedure, you can immediately return to your normal lifestyle.
How is the procedure performed?
Just like before a standard magnetic resonance imaging scan, you need to get rid of all metal objects. When using a contrast agent for several days before the examination, it is not recommended to eat foods rich in carbohydrates and increase gas formation. Five hours before the procedure you should not drink or eat; you can take an antispasmodic half an hour before the procedure.
Before administering the contrast agent, it is necessary to conduct a small test to identify hypersensitivity to gadolinium salts. To do this, apply a small amount of liquid to the back of the wrist. If after a few minutes there are no signs of an allergic reaction, you can begin the examination.
Typically, the contrast agent is administered intravenously
A contrast agent is injected into a vein, the amount of liquid depends on the age and weight of the patient. You may feel slightly dizzy after the injection. In some cases, the substance is administered dropwise, at a given speed, and using an infusion pump.
During the examination, you cannot change your body position or move. The average procedure time is about half an hour, but this depends on the type of device and the “problem” organ.
If all recommendations are followed, there is no harm in using contrast agents. They will quickly be eliminated from the body without leaving any traces. With the help of timely research, a number of dangerous diseases requiring immediate treatment.
For quick and effective diagnosis, MRI with contrast is often prescribed. This method has many advantages that make it indispensable in modern medicine. There are no barriers for him; he will look into all the patient’s organs without causing him any injury.
Every year, doctors increasingly prefer MRI as a diagnostic method. This is due not only to improved equipment in clinics and hospitals, but also to the undoubted advantages of the method, which include:
- non-invasiveness. There is no need to perform an exploratory operation or give the patient anesthesia. The only unpleasant procedure is an injection into a vein to install a catheter through which contrast is supplied. The most effective delivery of the drug to the tumor is intravenous;
- independence of results. The study is carried out automatically, the images are processed by a computer program. The human factor is reduced to a minimum, this is what makes them fundamentally different from ultrasound;
- MRI with and without contrast allows you to take clear images. It is possible to recreate a three-dimensional image of an organ or vascular system and rotate it on a computer screen. However, the contrast agent increases the information content of the scan results and allows you to see tumors and metastases at an early stage;
- The operation of the tomograph is based on the impact magnetic field on the body. It is considered absolutely harmless, although it exceeds the Earth’s own magnetic field tens of times;
- There is no limit on the number of MRI scans. Even if contrast agents are used, the contrast used in MRI does not accumulate in the body;
- the examination time is relatively short, scanning takes up to 40 minutes;
- if there are no contraindications, then contrast agents are safe for health;
- widespread equipping of clinics with tomographs leads to a reduction in the cost of the procedure and its waiting time;
- No lengthy preparation is required for MRI with contrast agent.

During a scan of the patient's body, more than a million images of slices are taken under different angles. The thickness of one slice does not exceed a couple of microns (for comparison, a micron is 1000 times less than 1 mm). Thanks to this, it became possible to recreate any organ and the smallest capillary after computer processing of images. All images that the computer shows are clear and precise, visual and detailed. They enable the attending physician to make the correct diagnosis. MRI can be performed with or without contrast.
Despite such an impressive list of advantages of the MRI method, it has disadvantages, which in certain cases become contraindications for the study:
- It is difficult to examine organs that are filled with gas. Such organs include, for example, the lungs and intestines;
- The effect of the contrast agent on the child’s body is unknown, so nursing mothers should refrain from feeding for a period of 24 hours;
- Kidney stones and some bone pathologies are not visible on the pictures;
- Even the slightest movements of patients can lead to the appearance of artifacts in the images. Computer programs are able to eliminate those that appear during the patient’s quiet breathing, while other movements will lead to incorrect results;
- Only trained specialists can operate the tomograph.
Limitations and contraindications in MRI
MRI has several limitations that are related to the design of the device:
- obese patients weighing more than 120 kg will not fit into the tomograph;
- There are special requirements for the rooms where scanning is carried out: it must be completely isolated from electromagnetic fields;
- MRI contrast agents can, in rare cases, cause short-term headaches and dizziness. Therefore, it is not recommended to drive immediately after the procedure.
To put it simply, MRI is a powerful magnet. This method is associated with contraindications:
- the patient has an artificial pacemaker, vascular clips, a pacemaker, metal permanent prostheses, i.e. everything that can be magnetized. These are absolute contraindications, because even the slightest shifts of the implants lead to serious injuries;
- tattoos on the patient’s body made using a dye that contains a ferromagnetic component will lead to severe burns;
- relative contraindications – pregnancy in the first trimester. During this period, all the internal organs of the fetus are formed, so any interference in this process is unacceptable;
- It is not recommended to scan unconscious patients;
- The patient has severe claustrophobia. In some cases, they are given a strong sedative.
However, in most cases, doctors prefer plain MRI or MRI with contrast agent because its advantages outweigh the disadvantages.
Why do you need contrast agent in MRI?
So what is an MRI with contrast and what is it for? Simply put, the process of performing the procedure is no different from a similar procedure for performing an MRI without contrast. The use of contrast agents (for example, Omniscan) improves the quality of images obtained during scanning.
They are administered to the patient intravenously during the study. They are quickly spread by blood throughout the body, accumulating in tumors, because the blood flow to them is usually stronger. The use of contrast allows for much better visualization of vessels and capillaries. This is especially true when studying blood vessels, the brain or spinal cord, and pelvic organs.
What is the difference between scanning with and without contrast? Usually the first MRI procedure is done without contrast, unless there are special indications for this. If, based on the results of the study, the doctor still has or has new questions, then an MRI with contrast is prescribed.
But in some cases, a tomography with contrast is immediately done. Most often this happens when it is necessary to examine the patient's vessels. Without contrast, they are much worse visualized in photographs.
MRI with contrast agent is indicated in the following cases:
- if there is a suspicion of malignancy. The contrast will “highlight” it, its contours and dimensions will be visible, and its location in the organ can be reliably determined;
- it is necessary to check the functioning of blood vessels;
- if monitoring the patient’s condition after surgery is required.
What is used as contrast in MRI?
The main active ingredient of modern contrast agents (Omniscan, Gadovist, Dotarem, Magnevist) is gadolinium salts. Although it is a heavy metal, it does not accumulate (like lead, for example) in the body; after testing, it is excreted from it by the kidneys within a few hours. Gadolinium salts dissolve well in water and are quickly distributed through the circulatory system. The most effective administration of drugs into the patient’s body is through a vein.
Quite rarely, patients experience side effects. The drug is well tolerated, side effects are extremely rare.
Gadolinium is a rare earth element and is extremely scarce in nature. Therefore, the cost of drugs such as Omniscan is high. It should be noted that side effects are extremely rare when using this drug.
Contraindications to MRI with contrast
Despite the good tolerance of drugs based on gadolinium salts, it should be noted that this is a toxic drug. Therefore, it is not recommended to be administered to people who have one of the following diseases:
- renal failure,
- liver diseases;
- heart failure;
- severe form of anemia;
- bronchial asthma.
Contrast agents used for MRI rarely cause allergic reactions, however, they should be used with caution in patients with diseases such as renal failure, epilepsy, bronchial asthma, and heart failure. Contrast-enhanced MRI is not recommended for pregnant women and nursing mothers. The effect of gadolinium on children has not been studied.
Preparing for MRI with contrast and conducting the study
Many patients are concerned about preparing for an upcoming study. A particularly common question is whether it is harmful to have an MRI, whether it is possible to eat before an MRI, and whether it is possible to eat immediately after it if a contrast agent is used. According to the instructions for use of the Omniscan drug, the main preparation for scanning is to stop eating and drinking 2 hours before the procedure. This can be attributed to the undoubted advantages of the drug Omniscan.
However, patients are often asked to eliminate foods that cause increased gas formation, for example, cabbage, peas, baked goods and similar products for 2-3 days. On the day of the study, it is recommended to refrain from eating large meals. light breakfast allowed.
When entering the room where the study is being carried out, the patient is required to remove all jewelry, watches, leave keys, wallet, mobile phone, remove clothing with metal elements. Some clinics provide hospital gowns that do not contain metal parts.
Immediately before the scan, the doctor will talk with the patient. He will take the test results, review your medical history, and whether preparations have been made for an MRI study with contrast. During this consultation, he will tell you how the procedure goes, what the patient will feel and hear, what to do in unforeseen situations, and whether it is possible to eat immediately after it.
After the patient signs informed consent for the MRI, a nurse will come and install a catheter in the vein. Before administering contrast to the patient, she may perform allergy tests on the back of the hand. To do this, a drop of the drug is applied to it. If there is no reaction within 5–10 minutes, which means there is no allergy, continue preparing for the MRI.
The amount of drug required to perform a scan directly depends on the patient's body weight. The standard dose is 0.2 mg of the drug per 1 kg of patient weight.
When the patient is placed in the CT scanner, the drug will begin to flow through this catheter. At the end of the test, the catheter will be removed and the patient will be asked to wait in the hallway for the results.
After the procedure
As a rule, the patient leaves the clinic with the scan results in hand. He no longer has restrictions on the amount of food and drinks he consumes. In rare cases, he may experience side effects from the contrast agent. These include:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- redness and itching at the injection site.
Despite all the shortcomings, limitations and possible reactions, MRI has become an indispensable method for diagnosing diseases. Side effects from contrast are extremely rare, and the benefits of the study outweigh them. The limitations of the method should be discussed with your doctor. As a rule, it is possible to select conditions when these restrictions are lifted.
MRI is a high-tech method for diagnosing diseases of the musculoskeletal system, internal organs, nervous and circulatory systems. The data obtained from such an examination is very accurate - tomography gives full information about the state of the body. But sometimes only an even more detailed method - MRI with contrast - will make it possible to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment in a timely manner.
Magnetic resonance imaging has a special principle of operation, it does not cause harm to the human body and does not cause disruptions in the functioning of organs and cells. As a result of the interaction of the magnetic field with the hydrogen atoms of tissues, high-precision sensors capture their response, and a powerful computer converts the received information into images. Layer-by-layer three-dimensional images of organs can show the doctor absolutely any deviations in the structure and functioning of any zone of the body.
Most often, MRI without contrast is used - a method that gives fairly clear images, their quality is much higher than that of inexpensive techniques (ultrasound, radiography). Even without contrast enhancement, tomography will allow visualization of the area of inflammation, degenerative lesion, bleeding or tumor. But sometimes it becomes necessary to use MRI with contrast. What is this study? Let's take a closer look.
MRI with the introduction of a contrast agent differs from a conventional scan in that during the process the contrast of some body tissues changes compared to others. For this purpose, a contrast agent is injected into the blood - a special drug that will react appropriately to the tomography. MRI with contrast is necessary to reflect tissues in different color shades, which will give the doctor the opportunity to make an accurate diagnosis.
Indications for the procedure
According to statistics, the use of a contrast agent in MRI is shown in approximately 1/5 of all studies of this type. If the doctor recommends performing an MRI with contrast, there must be clear indications for this. The main indication for the administration of a contrast agent is the need to differentiate a cancerous tumor from a benign neoplasm. Such research will also be needed to more precise definition areas of metastases to assess the effectiveness of tumor removal.
What else does an MRI with contrast show? This:
- Inflammatory changes in soft tissues.
- Condition of blood vessels, anomalies of their development.
- Zones of localization of atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots.
- Increase and decrease in the size of organs and their individual parts.
- Areas of damage, injury, organ degeneration.
- Intervertebral hernias (mainly to assess their condition after surgery).
Thus, the dye is an indicator of pathological processes and phenomena in the body. It accumulates in diseased tissues, allowing one to obtain detailed pictures and draw the necessary conclusions. This type of tomography is often prescribed after a conventional MRI if there is insufficient information.
What is used for contrast?
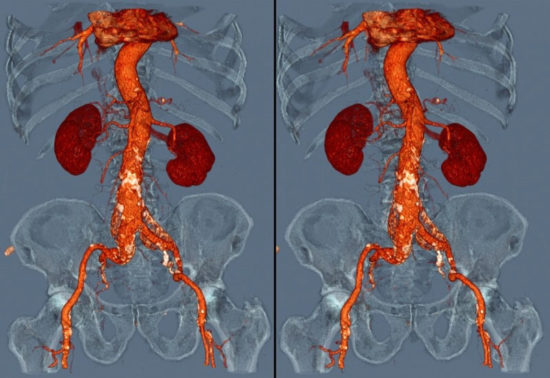
The MRI contrast agent most often used in medical practice is called gadolinium. This is a silvery metal, a lanthanide, with increased viscosity and softness. Gadolinium has seven unpaired electrons, which facilitate rapid transmission of signals during examination. The toxicity of this substance is low, and yet gadolinium causes allergies in some people. After an MRI with a contrast agent, they develop:
- Erythema and various types of skin rashes.
- Hives.
- Headache, dizziness.
- Nausea.
- Shortness of breath, difficulty breathing.
- Itchy throat, nose.
- Sneezing, watery eyes.
IN last years Extensive research has been carried out to reduce the allergenicity of gadolinium, and now, not its saline solutions, but chelate complexes are predominantly used. Their toxicity is minimal, and there are almost no pronounced side effects. The risk of allergies approaches 0.1%. The best drugs are considered:
- Omniscan
- Gadovist
- Dotarem
- Premovist, etc.
How is the contrast agent administered?
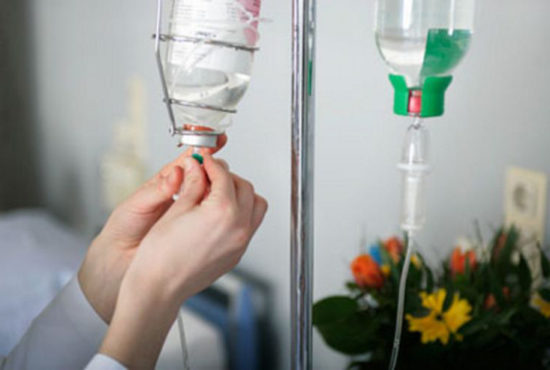
To successfully complete the study, the drug must be administered correctly. Therefore, before starting the procedure, the person is weighed in order to accurately calculate the dose of contrast (0.2 mg per kilogram of weight). There are two ways to introduce it:
- Intravenous. The drug is administered once into a vein. The required level of contrast agent in the blood is achieved within a few seconds.
- Bolus. In this case, the drug is administered using a special device (automatic injector), the rate of administration is strictly fixed and determined by a specialist.
Typically, the second contrast method is used to assess the condition of blood vessels and search for pathologies of parenchymal organs.
How is an MRI performed?
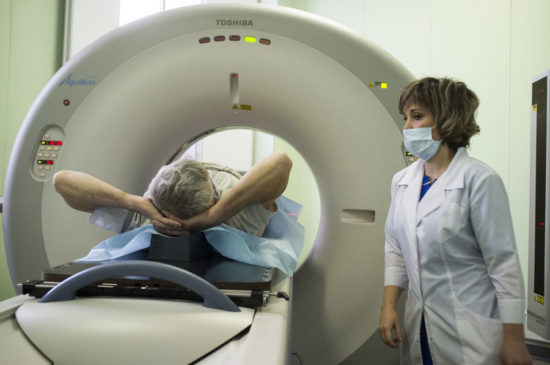
Preparation for the examination will largely depend on which area of the body is being examined. But before any type of tomography with contrast, it is not recommended to eat 6-8 hours before the diagnosis. During MRI of the peritoneum, you should not eat foods that increase gas formation 2 days before the procedure. Allergy sufferers should take a long-acting antihistamine tablet in the morning.
Immediately before the MRI, all metal jewelry and removable dentures must be removed. Clothes should be loose. The patient lies down on the couch and is injected with a contrast agent. If tomography has not been performed previously, regular images are taken first, and then contrast is administered. The patient is placed under the arc or cylinder of the tomograph and the examination is completed.
It can last, depending on the zone, from 15 to 50-70 minutes.
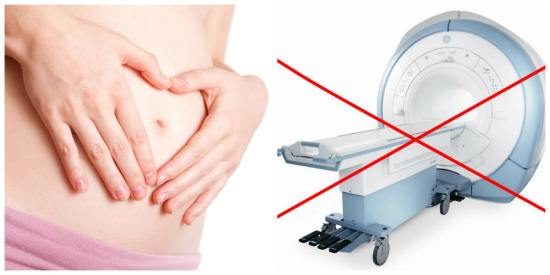
In patients with severe kidney pathologies, after the administration of contrast, the development of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is occasionally observed, so this procedure is extremely undesirable for them. The following conditions are also relative contraindications to the study (they require medical consultation):
- Bronchial asthma
- Allergic diseases
- Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels
- Severe dehydration
- Some types of anemia
- Use of beta blockers and certain other medications
- Pregnancy
- Recent vascular surgery
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the administration of contrast is undesirable, but in some situations it is still possible. The use of contrast in the first 14 weeks of pregnancy is strictly prohibited. For mental disorders or claustrophobia, the procedure can be performed with sedation or anesthesia. Magnetic resonance imaging is contraindicated in the presence of metal devices and instruments in the body. Enhanced MRI is also prohibited for children under 3 years of age, but is performed for health reasons.

- Benign tumors – cysts, polyps, papillomas, fibromas of the central nervous system, internal organs
- Cancer tumors and metastases of any area of the body
- Encephalitis
- Meningitis
- Thrombosis
- Thromboembolism
- Vascular atherosclerosis
- Venous, arteriovenous malformations
- Multiple sclerosis
- Spinal cord pathologies
- Pituitary adenoma
- Dropsy (ascites) of the peritoneum, lungs and other organs
- Stagnation of bile in the common bile duct
- Pathologies of the hepatobiliary system
- Diseases of ligaments and cartilage
Contrast in MRI
Modern diagnostics has a rich toolkit of methods and techniques, but the most accurate is magnetic resonance imaging or MRI. Since the advent of this high-tech tool in 1973, many lives have been saved. It radically influenced diagnostics in general, as it made it possible to look inside a person in detail, more accurate than X-rays and CT scans provided. MRI allows you to obtain layer-by-layer images of organs several microns thick. The computer transforms these images into a three-dimensional model. The preliminary diagnosis dictates the area of study. But sometimes, for greater diagnostic sensitivity, the doctor recommends an MRI with contrast, which involves intravenous administration of paramagnetic contrast compounds. Patients often have questions: “What is MRI with contrast? And how is it different from the usual one?”
What is MRI with contrast?
During an MRI with contrast, the patient is injected with a special dye, which allows the image to better highlight the area being examined. This is especially true when diagnosing malignant neoplasms, since the contrast, settling in the tumor cells, gives greater clarity to the contours, size, structure of the tumor and its metastases. The speed of blood circulation in the study area affects the distribution time of the dye and the strength of the magnetic signal.
Contrast agent for MRI - types and properties
Contrast agents can be hydrophilic complex compounds with a high concentration of gadolinium cations. Substances from the group of magnetic pharmaceuticals differ from those used in radiography. They are less toxic than contrast containing iodine salts and compounds used in CT and fluorography. Allergies to gadolinium compounds in the form of itchy eyes and hives are extremely rare. If a reaction does occur, it is milder and easily cured. Improved visualization is achieved due to the fact that gadolinium enters the soft tissues through the blood vessels and accumulates there. The peculiarity of gadolinium is its ability to enhance the magnetic signal during MRI, which improves the quality of images. There are many contrast agents. They are conventionally divided into the following groups:
- Intravascular. The dye is injected into the vein in full. The calculation is carried out using the formula 0.2 mg/kg of weight. These may be substances based on iron oxide, which has superparamagnetic properties. This also includes manganese compounds.
- Bolus contrast. The dye is also administered intravenously, but in doses through a dropper. The tomography progress and pigment supply are synchronized.
- Using oral agents, the gastrointestinal tract is scanned. In addition to manganese and gadolinium compounds, some natural products, for example, blueberry and green tea behind high content manganese
Dye tomography is more expensive than conventional tomography, but is well worth the higher cost.
Indications for tomography with contrast
Today, 1/5 of MRIs are performed using contrast. The decision to perform an MRI with or without contrast is made by the doctor. This method is preferable in the following cases:
- malignant neoplasms;
- suspicion of infection and inflammatory process in organism;
- multiple sclerosis;
- meningeal pathologies;
- problems with the spine;
- abnormalities of the digestive system;
- as a continuation of the study conducted without the use of a dye.
Contraindications to MRI with contrast
Negative effects of the dye during the study were excluded. It does not lead to complications after the procedure. There are few contraindications, these are:
- the first 3 months of pregnancy due to the special susceptibility of the fetus;
- individual intolerance to any component of the coloring matter;
- bronchial asthma;
- renal and liver failure. Nephrogenic fibrosis may result from the use of gadolinium;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- dehydration of body tissues;
- taking certain medications, for example, β-blockers.
In all other cases, including children, tomography with contrast can be performed. Sometimes circumstances force you to do an MRI using dye even to the expectant mother. Contrast agents are excreted in feces and do not have any side effects on the health of the subject. Factors unfavorable for the study cannot be considered as definitive. The decision on admission is made by the doctor treating the relevant pathology.
Preparing for the study
There are no fundamental differences in tomography with contrast compared to conventional one. But there are several general recommendations before it is carried out:
- Before the examination, it is necessary to remove all objects made of metal. Mobile phones cannot be brought into a room with a magnetic installation.
- You should not use cosmetics, as metal microparticles can worsen the test result. The doctor should also be aware of the tattoos on the patient’s body.
- Dentures can also be removed.
Additional preparation will be required when examining organs abdominal cavity- 5 hours before the scan you will have to give up food and water. An hour before the examination of the pelvic organs, you need to drink 1 liter of water for greater reliability of the results. After preliminary images obtained without dye, an injection is performed, for which the laboratory assistant injects 20 ml of dye intravenously. After an MRI with contrast, the doctor compares the results of the studies to obtain maximum information about the condition of a specific area and make the correct diagnosis. And this is the first step on the path to recovery.
Approximately 20-30% of MRI examinations worldwide are performed with contrast. Most cases of contrast tomography are used for oncological diagnostics. The industry requires detection of the smallest neoplasms at an early stage, when pathological foci are not visually identified on tomograms. Only the identification of newly formed vessels allows one to suspect a tumor or metastasis.
How MRI contrasts work
Contrast enhancement increases the strength of the MR signal. Intravenous injection of paramagnetic compounds significantly increases the visibility of the area in which the substances are located.
Regardless of the type of contrast, they are made based on the rare earth metal gadolinium. In its pure form, the mineral is toxic, but in a strong complex with chelates it is absolutely harmless to the human body.
A slight difference in the composition of Gadovist, Omniscan, Dotarem, Magnevist allows the use of these MRI contrast agents for different types research (brain, internal organs, pelvis). The degree of enhancement depends not so much on the type of substance, but on the correct dose and the intensity of blood supply to the area under study. Primovist and Gadovist are administered at a dose of 0.1 ml per kilogram.
Qualitative enhancement with Omniscan and Gadovist is achieved by calculating the injection in the ratio of 0.2 ml of the product per 1 kilogram of weight.
How is contrast enhancement performed in magnetic resonance imaging?
Depending on the purpose of the examination, one of the types of contrast is used:
- Bolus;
- Classic.
With bolus enhancement, MRI contrast fluid is administered intravenously or using an automatic syringe. The procedure allows you to visualize the desired area at the required time intervals.
Dynamic MRI with contrast, Gadovist or Magnevist, which is prescribed most often in Europe, includes synchronization of the drug injection and the scanning step. The procedure is combined with bolus enhancement.
It is not difficult to determine which contrast agent is administered using the classical method (Primovist, Magnevist, Omniscan, Gadovist). The only difference is in the calculation of concentration. The technique is based on the introduction of the compound some time before tomography.
Your doctor will be able to choose the right contrast agent to use for MRI of the desired area. radiology diagnostics. Before the examination, consultation with a specialist is necessary. Statistics have recorded the use of Magnevist in magnetic resonance imaging in 45 million cases - which is the maximum percentage of all contrast agents.
Contraindications to the use of MRI contrast agents
If you want to buy contrast for MRI at a pharmacy, you should pay attention not only to the gadolinium content, but also to the intended type of examination.
For example, gadobutrol, even in small doses, significantly improves T1 and T2 weighted imaging, which is used to scan the brain and spinal cord.
If Omniscan, a contrast agent for MRI, is used for kidney disease, the likelihood of complications increases. For pyelonephritis, it is better to use a single-molar compound - Gadovist or Primovist at a dosage of 0.1 ml per kilogram.
- Decreased renal filtration (creatinine clearance below 30 ml per minute);
- Pregnancy (most of the substance passes through the placental barrier);
- Allergic sensitivity to gadolinium.
When choosing an MRI contrast whose name is unfamiliar, you need to study the manufacturer's instructions. Most drugs have no practical studies on their effects on children under 18 years of age. Gadovist is not used in cases of low seizure activity or a tendency to be allergic to gadolinium.









