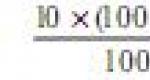What's the difference between revenue and gross income? Difference between revenue and profit
Net profit and net income are two, at first glance, identical concepts. All the subtleties of the terms have been studied in detail by economists, thanks to the study of a huge amount of specialized literature. But it wouldn’t hurt for an ordinary person to know, at least in general terms, what the fundamental differences between the concepts are, especially if opening their own business is on the horizon. It is difficult to judge the profitability of a business if you take income and profit as interchangeable synonyms.
Distinctive features of the concepts of net profit and income
Net profit is considered balance after all transactions for a specific period of time, in other words, financial resources after deducting various production costs, taxes, possible fines, credit interest, and so on. It is a source for creating reserve funds and deductions for production processes.

Stable profit growth has a beneficial effect on capital turnover. This is the final indicator of the performance of a company or enterprise, which is reflected in the accounting report and affects the amount of winnings of the owners. Profit is classified:
- By distribution costs (economic, accounting).
- Based on the results of the enterprise’s activities (normative, lost, maximum possible).
- Depending on taxation (taxable and non-taxable).
Net income refers to absolutely all monetary and material resources received into the account of an individual, legal entity, institution or state for a certain period of time. Income is generated by the amount resulting from trade, sales of products, services and core activities. The amount of income depends on the cost of the product and the situation on the sales market as a whole. The amount after taxes is paid is distributed to:
- Income generated as a result of investment operations.
- Employee wage costs.
- Insurance premiums.

An elementary example of determining net profit and income
Formulas for calculating the quantities under consideration in general look quite simple:
- Net income = All revenue for a specific time.
- Net profit = Net income - all costs of production and sales for a specific time.
Thus, net profit is the difference between net income and all kinds of expenses. For greater clarity, we can give a simple example. To open a small grocery store, some premises are rented. During the first month, the cash register received 700 thousand rubles. - this is net income. But it’s too early to talk about profitability and payback. It is necessary to understand that approximately the following deductions will follow from the money received:
- Payment of taxes.
- The cost of renting the premises.
- Utilities (eg electricity, water supply).
- Staff salaries.
- Transport costs.
- Purchase goods for the next month.
- Payment of interest for using credit funds (if the owner needed them to open his business).
- Product and store advertising.
In addition to those listed above, other types of expenses are possible. After carrying out the appropriate calculations, the following results are summed up:
When subtracted from 700 thousand rubles. there is nothing left, and the private entrepreneur has to use personal savings to make all payments. The current situation only shows that the business is unprofitable. The option of closing it should be considered.
It is possible that after all the deductions there is nothing left, but there is no need to use additional funds from outside. We get zero profit. This situation indicates that the entrepreneur has reached the break-even point. Marginal profit is possible due to the sale of additional goods. But good performance in this case does not always indicate high profits in reality. In addition, if prices for a range of goods are reduced, the profitability of the business as a whole is undermined. This technique should be practiced for a short time and not for all products.
The most favorable outcome is if, after the necessary deductions and expenses, there is still some amount left, for example 200-300 thousand rubles. The owner subsequently invests it in the development and expansion of the store or spends it as he deems necessary. The presence of net profit as a result of the activity and its value indicate the profitability of the business.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that net profit is significantly less than income. In the practice of private entrepreneurship, it is always a decisive indicator and is of greater importance. Steadily growing profits are what we need to strive for in private entrepreneurship.
Revenue, income and profit: what is what
It is difficult to assess the efficiency of an enterprise; the criteria are chosen differently in each case. But always, both when planning and when analyzing current activities, financial indicators are used. Among the mandatory ones are revenue, income and net profit. These concepts are often confused.
Revenue
Revenue refers to funds received for products sold or services provided. There are 2 ways to reflect revenue:
- cash method;
- accrual accounting of revenue.
The cash method assumes that only money actually received is included in revenue. It shows how much the company already manages. But revenue also includes advances for which the company has not yet fulfilled its obligations.
In accrual accounting, revenue is recorded at the time the goods are shipped or the service is provided. In this case, the indicator shows sales volume, but does not take into account the fact that the buyer may be dishonest and will not pay for the purchase.
From an accounting point of view, the company’s revenue is divided into 2 types:
- gross;
- clean.
Gross revenue is the payment received for a product or service sold. Net proceeds are gross proceeds minus excise taxes, taxes, fees and duties directly included in the price of the goods. It is reflected in a mandatory document - the profit and loss statement.
The revenue indicator does not reflect the company’s operating efficiency, because revenue also comes from unprofitable enterprises, but it characterizes the company’s share in the market. To calculate this share, you need to know the sales volumes in the industry for the reporting period.
Income
Income includes all receipts, not just those related to the company's core activities. This includes interest on deposits or collected fines and penalties.
If revenue is strictly planned, then income may be unplanned, for example, if a partner violated the terms of the contract and paid a penalty.
Profit
Profit is the basic indicator for assessing the performance of an enterprise. It is this that primarily interests shareholders, because dividends are paid from profits.
Gross and net
There are gross and net profit.
Gross profit shows the overall performance of a business. To calculate it, you need to subtract costs from income for a certain period. Banks and the state will also want their share of this “pie.” Therefore, company shareholders pay attention to net profit.
Net profit is what the company works for. It is not necessarily paid out in full to shareholders. To calculate net profit, mandatory payments are subtracted from gross profit:
- taxes, fees and fines (that part of the “total” profit that is due to the state);
- interest payments (goes to the financial institutions that issued the loan to the company).
The remaining money is called retained earnings. They are reinvested, that is, used for the benefit of the company. This is an alternative to a bank loan or other external financing. How much money to give in the form of dividends and how much to spend on development is decided by the meeting of shareholders.
If the net profit is negative, it is called an uncovered loss. Until profits cover losses, the company does not pay income tax.
EBITDA and EBIT
There are 2 more profit indicators that are not reported, but are used in financial modeling, when evaluating projects, and are of interest to investors: EBIT - earnings before interest and taxes, and EBITDA - earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization.
EBITDA was originally created to measure whether a company can pay off its debts. This parameter, together with the net profit indicator, reflects the amount of payments that the company will make in the fixed-term period.
It illustrates the income that a company receives in the current period. It is easy to carry forward to future periods, so it is used to assess the return on investment and the possibility of self-financing.
EBITDA allows you to compare companies regardless of type and accounting policies. The comparison is not affected by the size of the investment, the loan burden and the tax regime.
The main disadvantage of the EBITDA parameter is that it does not take into account that the company will need money to replace equipment due to depreciation. Enterprises that spend a large share of their costs on depreciation (heavy industry, extraction of natural raw materials, construction) try to demonstrate this parameter more often, because this way their projected profit is more attractive to investors. Therefore, investors consider EBITDA along with EBIT.
Another drawback of EBITDA and EBIT is that the calculation takes into account not only the results of core activities, but also one-time income. This makes it difficult to analyze the company. To get rid of such “information noise,” other income is subtracted in calculations or operating profit is used. This predicts the firm's ability to generate cash flow. But the problem is that these additional transactions can cause financial manipulation, and the indicators will ultimately be overestimated or underestimated.
The activities of a commercial organization can be characterized by its revenue and sales. What is their specificity?
What is revenue in a business?
The revenue of a commercial enterprise is usually understood as the amount (or a list of property in value terms) that it received as a result of sales or provision of services within a certain period of time. Based on the difference between revenue and expenses (and sometimes only on the basis of the value of the first indicator), the amount of taxes that the company must pay to the state is determined. The exception is the taxation mechanism, in which the corresponding cash receipts to the enterprise account are not taken into account: such schemes include, for example, the UTII system provided for by Russian legislation.
It is worth noting that, in accordance with some financial analysis methods, revenue as an economically significant indicator can be reduced by taxes (in this case it is called “net revenue”).
A common approach according to which revenue is classified is:
- on cash receipts from the main type of commercial activity of the company;
- on proceeds from investments (for example, in the form of proceeds from the sale of securities);
- on revenue generated as a result of changes in exchange rates (for example, when exporting goods).
All three types of financial income are combined into total revenue. But, as a rule, business efficiency is assessed based on the income that is associated with the main activities of the enterprise.
A company's revenue can be calculated using two methods: cash and accrual. In the first case, it is recorded upon the fact that the enterprise accepts funds into its current account or cash register. In the second, it is calculated when the buyer of goods or consumer of services has obligations confirmed by contract or law related to payment for delivered products or services.
The main condition for receiving revenue from the main activity, regardless of the specific method of its calculation, is the sale of goods or services. Let's consider its specifics in more detail.
What is implementation?
This term corresponds to the direction of activity of a commercial enterprise, which is associated with the supply of goods or services produced or resold by it to the market. In fact, we are talking about meeting the demand generated by consumers. At the same time, the interaction between them and suppliers within the framework of sales may involve not only the actual purchase and sale of goods or services, but also, for example, the organization of their delivery (providing conditions for provision, if we are talking about services), storage, promotion through available channels sales, etc.
The end result of the sale of a product or service is the receipt by the authorized person of payment for the deliveries made, which, in fact, forms revenue from the main activity (or, if we are talking about the cash method of recording income, this will be the buyer’s acceptance of obligations to pay for the product or service) . 
It may be noted that, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, the following cannot be recognized as sales, in particular:
- operations related to currency circulation;
- transfer of the company's resources to its legal successors as part of the reorganization of the business entity;
- transfer of company resources to non-profit organizations for non-commercial activities;
- transfer of investment property under a partnership agreement, as well as to mutual funds established in cooperatives;
- transfer of property within the framework of concession legal relations;
- transfer of resources of a business company to one of the participants upon his exit from the business;
- transfer of apartments to citizens as part of privatization;
- operations of seizure of property, handling of ownerless things.
Comparison
There is more than one difference between revenue and sales. This is due to the fact that these terms, although used, as a rule, in the same context, nevertheless mean different things.
Revenue is the flow of cash received by an organization as a result of commercial activities. However, it is not always related to sales. Revenue, as we noted at the beginning of the article, can be, in particular, investment income.
Implementation- this is the part of commercial activity that is most significant from the point of view of the company’s acquisition of revenue from its main type of business. It is almost always associated with sales of goods and services.
Having determined what the difference between revenue and sales is fundamentally, we will reflect the conclusions in a small table.
Revenue (revenue) - the total amount of money received (proceeded) by a company, entrepreneur or receivable for a certain period of activity from the sale of the subject of commercial activity - goods and (or) services.
Revenue is the amount of money received in a given period from the sale of products, for work performed, services provided, from the rental of real estate, minus turnover tax. V. from the sale of products depends on the quantity of products produced, their composition (assortment, nomenclature) and wholesale prices. V. is used in calculating the gross income of an enterprise.
Purpose of revenue generation. Sales revenue is the company's main source of reimbursement for the funds spent on production. Timely receipt of revenue ensures the stability of the company, the continuity of the turnover of funds, and the uninterrupted commercial activities of the company. The proceeds are used to pay suppliers' bills, spare parts, fuel, and energy. From the proceeds, wages are paid, depreciation of fixed assets is compensated, and the profit of the enterprise is generated. Late receipt of revenue leads to interruptions in business, decreased profits, violation of contractual obligations, and penalties.
Revenue forecasting- determination of the possible (taking into account the probability) achievement of the volume of proceeds, with planned measures to ensure revenue and a certain forecast market reaction to the offer of goods and services of the company.
Total revenue consists of revenue from the results of three areas of activity:
- revenue from core activities coming from the sale of products (work performed, services provided);
- revenue from investment activities, expressed in the form of financial results from the sale of non-current assets, sale of securities;
- revenue from the company's financial activities.
Revenue calculation methods. In commercial accounting, two methods of calculating revenue are used:
- cash basis revenue- determination of revenue based on the actual receipt of funds into the company’s cash accounts. Revenue is considered to be payment received to the accounts or cash desk of the enterprise or goods received in payment of obligations (barter);
- revenue on accrual basis- revenue is accrued when consumers have obligations to pay for the company’s products or services. Revenue is calculated without the actual receipt of funds into the cash register or into the company's accounts. Most often, revenue is accrued at the time of shipment of products or provision of services to the buyer.
Revenue from turnover- the first item of income in the profit and loss account: revenue from sales of goods and services within the normal course of business. .
Gross revenue- this is the total cash income equal to the amount of cash received from the sale of products, income from non-sales operations, as well as other property.Sales revenue- funds received by the enterprise (receivable) for products shipped to customers. Sales proceeds are divided into gross (total) and net. The gross revenue of an enterprise (manufacturer) is the cost of products sold. Net revenue represents gross revenue minus VAT, discounts, cost of goods returned by customers, and excise taxes.
Number of impressions: 71762