The thyroid gland is enlarged and hormones are normal. Enlarged thyroid gland. Causes of enlarged thyroid gland.
Thyroid gland– irreplaceable organ endocrine system, which produces substances responsible for many important processes. Namely, it is responsible for brain activity, cardiac activity, muscle tone, and metabolic processes. Therefore, any problems with the thyroid gland sooner or later are reflected in other organs and systems.
Enlarged thyroid gland - causes
Very high magnification thyroid gland may cause disability in the airway or esophagus. If increased thyroid gland compresses the so-called. retrograde laryngeal nerve, the patient may experience other phonogram disturbances. Iodine deficiency causes sensitization of thyroid cells to local growth factors, which leads to an increase in their absolute number. In turn, stimulation of thyrocytes by the thyroid gland secreted by the pituitary gland leads to hypertrophy. A similar situation arises when dietary products consumed in the diet, i.e. substances that limit the absorption of iodine from food or affect the metabolism of this element. Tumors may also appear clinically as open enlargement of the thyroid gland. Thyroid hyperplasia in Graves-Bayev disease results from stimulation of circulating antibody-mediated thyrotropin receptors on the thyroid gland. Stimulation of these receptors by these antibodies also contributes to the development of the full clinical picture of hyperthyroidism. The initial stage of Hashimoto's, the most common cause of hypopituitarism, is almost always associated with an enlarged thyroid gland. Thyroid hyperplasia can also occur in cases of increased demand for the thyroid hormone thyroxine and triiodothyronine. This is the case, for example, during pregnancy, when chorionic gonadotropin, produced in large quantities by cyto- and syncytiotrophoblast cells, exhibits thyroid-like activity of the thyroid gland, promoting hypertrophy.
Increased thyroid therapy
- Almost 90% of cases worldwide are caused by iodine deficiency.
- In Poland, this cause occurs sporadically.
- Malignant tumors may be accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes.
- Graves' disease.
- The goose is usually quite coherent and palpation does not cause pain to the patient.
It has been established that thyroid diseases develop in women much more often than in the stronger sex, and one of the common pathologies is an enlargement of this organ. This is often due to a deficiency of iodine in the body, poor environmental conditions, constant stress, chronic infectious diseases, bad habits. Let's find out what the symptoms of diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland are and methods of treatment for this diagnosis.
Therapeutic management of thyroid enlargement must be targeted. If your thyroid is caused by iodine deficiency, you should supplement your iodine supply. Likewise, if an enlarged thyroid occurs with hyperthyroidism, enlargement of the thyroid gland may be helpful. antithyroid drugs or.
Depression, difficulty withstanding cold, depression, depressive symptoms, irregular menstruation, weight gain without changes in diet, swelling, constipation and slow bowel movements. One of the most common causes of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's disease, which is chronic. This is an autoimmune chronic disease that leads to the destruction of the thyroid gland and a decrease in its hormonal production.
Symptoms of an enlarged thyroid gland
Symptoms of an enlarged thyroid gland and its hormones do not appear immediately and depend on the stage of the pathology. Changes can only be noticed by palpation examination, ultrasound or radiographic examination. There are 5 stages of thyroid enlargement with the following symptoms:
- At the first stage, when palpating, the enlargement of the gland is not detected, however, while swallowing saliva and eating food, the patient may feel some discomfort.
- At the second stage, enlarged lobes of the gland are already palpable, and its enlarged isthmus is noticeable.
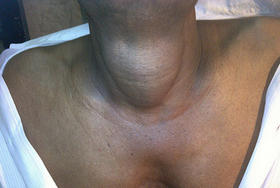
- The third stage is characterized by a visually noticeable size of the organ, as a result of which the neck thickens and its contours change.
- With fourth degree enlargement, the thyroid gland begins to protrude not only forward, but also to the sides. Swallowing functions become significantly more difficult.
- The most severe stage leads to disfigurement of the neck. The trachea and esophagus are compressed, as a result of which the processes of swallowing and breathing are disrupted, the voice changes, and the patient feels significant pain and discomfort.
The following manifestations may indicate an enlarged thyroid gland:
Other autoimmune thyroiditis, iodine deficiency or overconsumption, iodine treatment, some thyroid surgeries, congenital hypothyroidism in children whose mothers suffered from hypothyroidism during pregnancy, overdose of antithyroid drugs. Hypothyroidism can also adversely affect a child's later development.
Hypometabolic coma is a life-threatening condition during untreated and extremely severe hypothyroidism. This condition can sometimes be caused by a comorbid illness, which may include, for example, a systemic infection. Lack of specialized treatment increases the risk of death. The mortality rate in this case is quite high and is about 20%, usually due to diseases that lead to the metabolic breakthrough of the hip, rather than as a result of the breakthrough itself.
- weight loss or gain for no apparent reason;
- rapid heartbeat;
- fatigue, weakness;
- irritability;
- sleep problems;
- hair loss and dullness;
- sweating;
- irregular menstruation;
- visual impairment;
- unexplained cough;
- stool disorders, etc.
Treatment for enlarged thyroid gland
To prescribe adequate treatment for this pathology, it is first necessary to carry out the necessary diagnostic measures, including:
Thyroid nodules
A person suffering from hypometabolic breakthrough has limited contact with the surrounding reality or is completely comatose. There is hypothermia and therefore a lower body temperature, which in most cases is below 30 degrees Celsius and sometimes can even drop to 24 degrees. Other characteristic symptoms of this condition are sinus bradycardia, hypotension, hypoxia with hypercapnia, hyponatremia with symptoms of water intoxication, hypoglycemia, edema and dementia. Muscle tension decreases, but cramps may also occur.

Treatment methods depend on the causes of thyroid enlargement, the stage of the pathological process, and concomitant ailments. It is easy to guess that grade 1 enlargement of the thyroid gland is most easily treatable, so early detection of pathology is very important. In advanced cases, as a rule, it is not possible to do without surgical treatment.
Diagnosis of enlarged thyroid gland
Tendon reflexes are also weakened. Sometimes characteristic symptoms of coexisting diseases, such as pneumonia or other infections, may occur. Typical swelling of the eyes and widening of the tongue. Sometimes yellowing of the skin is also confirmed. Patients diagnosed with hypometabolic coma should be admitted to the intensive care unit. Treatment includes, first of all, adequate hormonal supplementation and equalization of metabolic disturbances. For this purpose, large doses of levothyroxine are administered intravenously.
In most cases, treatment involves drug replacement therapy - taking hormonal drugs. Drugs that inhibit the functioning of the gland and a special diet may also be recommended. One of modern methods treatment is radioiodine therapy - the use of radioactive iodine preparations to destroy gland tissue.
Levothyroxine, administered as a single infusion or using a special infusion pump, can cause noticeable clinical improvement very quickly, even after a few hours. In addition, the patient must be provided with good ventilation. Intubation and respiratory support are very common. Treatment of electrolyte imbalances and possible hypoglycemia is also used with proper treatment. However, hypotonic fluids should not be administered because there is a risk of water toxicity. Intensive treatment of concomitant diseases, especially heart failure and infections, is also necessary.
Treatment of enlarged thyroid gland folk remedies can be carried out only after diagnosis and with the permission of a doctor. Most effective traditional method Treatment of thyroid diseases is the use of alcohol tincture of white cinquefoil.
The thyroid gland is enlarged - a symptom that may indicate the presence of dysfunction not only of the organ itself, but also of the entire endocrine system, since the gland is responsible for controlling the metabolism of the entire body.
Thyroid gland in children
To achieve this, it is recommended to use empirical antibiotic therapy until culture results are available. In severe cases of disease or coexistence of adrenal insufficiency, it is advisable to take hydrocortisone. Hypothyroidism should not be actively heated, as this can cause blood vessels to dilate and go into shock. To prevent further heat loss from the patient, simply wrap the patient in a warm blanket.
Lugol's liquid can be taken for hyperthyroidism, not hypothyroidism! A deficiency will also interfere with the release of thyroid hormones. Believe it or not, read about the influence of Wolf-Chaikoff. Hyperthyroidism is a disorder in which the thyroid gland produces too many hormones relative to the body's needs. The thyroid gland is a small organ located at the base of the neck. It is responsible for the production and release of two hormones, triiodothyronine and thyroxine, which regulate the function of most body tissues, affecting our body's metabolism and thermogenesis.
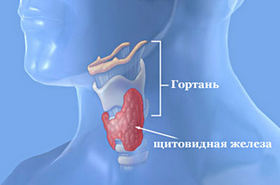
This important organ is located in the neck, slightly below the thyroid cartilage, on the sides of the trachea. It has two lobes connected by an isthmus.
Signs of pathology
Doctors distinguish 5 stages of this disease, each of which has its own symptoms:
- First stage. Upon examination, the lobes of the gland are not visualized, but during swallowing a small isthmus can be noticed. Palpation also reveals nothing
- Second stage. During swallowing, the lobes of the gland are visible and palpated. The contour and shape of the neck is still unchanged
- Third stage. The thyroid gland is enlarged, causing the neck to become thicker and change its shape. The lobes are very visible and can be felt during palpation
- The fourth stage is characterized by a change in the configuration of the neck due to a strong enlargement of the gland, the contours of which are already visible without palpation
- Fifth stage. The organ grows to such volumes that the trachea and esophagus are compressed, as a result, the process of breathing and swallowing is disrupted, and the voice changes or completely disappears.

The diagnosis of an enlarged thyroid gland, in other words, a goiter, is made in the last three stages. Sometimes the disease can occur without any symptoms and the patient consults a doctor only because of a change in the contour of the neck.
The thyroid gland is a small organ located at the base of the neck. The most common causes of hyperthyroidism in Poland are. Graves' disease and thyroid nodules. . Rare causes of hyperthyroidism include the following: subacute thyroiditis and post-thyroiditis.
How often does hyperthyroidism occur?
Hyperthyroidism is one of the most common endocrine diseases; Approximately 1-2% of adults in Poland.
How does hyperthyroidism manifest?
The main symptoms indicating hyperthyroidism are: The extent of symptoms may vary from patient to patient. In older people, symptoms of hyperthyroidism may be less severe. Weakness and cardiovascular problems may be predominant - cardiac arrhythmias, symptoms of heart failure.At the same time, the disease itself is already in an advanced form and may not respond to drug treatment.
In children, the appearance of this pathology is accompanied by rapid fatigue, decreased concentration, constant weakness the whole body. Classic signs of the disease in the form of an enlarged gland may be completely absent.
What to do if you experience symptoms?
The test is performed from a blood sample that does not need to be taken on an empty stomach. In cases of very severe hyperthyroidism, the patient must be rushed to the hospital. Hormonal testing is required to confirm hyperthyroidism. A preliminary test to assess thyroid function can be instructed by your family doctor. If the result is incorrect, the concentration of free thyroid hormones must be measured.
If you are diagnosed with hyperthyroidism, your doctor will try to determine the cause of the thyroid problem, which is important when deciding how to treat it. The following tests are useful for this purpose. There are many ways to treat hyperthyroidism. There is more than one best therapy because each method has advantages and disadvantages that you can discuss with your doctor. In addition, the treatment of hyperthyroidism depends on its cause, severity, age of the patient, and coexisting diseases. Hence, best method treatment is determined individually for each patient.
Organ diseases
Graves' disease (toxic goiter) - the thyroid gland is enlarged and there is an increased production of thyroid hormones, as a result of which the disease thyrotoxicosis appears.
There is a rapid increase in metabolism, leading to strong weight loss sick. The mammary glands and liver are affected, and diabetes may develop.
The degree of enlargement of the thyroid gland
This usually starts with the use of medications that reduce the production of thyroid hormones, usually with another treatment plan in mind. Hyperthyroidism should not be underestimated, untreated can lead to dangerous complications such as cardiac arrhythmias, heart failure, osteoporosis or thyroid disease. In pregnant women, hyperthyroidism is unfavorable for both the mother and the fetus. Treating hyperthyroidism requires following medical advice, regular medications, and regular checkups.
The main symptoms of this disease:
- fatigue with increased excitability
- tearfulness and touchiness
- dyspnea
- sleep disorder
- trembling throughout the body
- rapid heartbeat.
Nodular goiter is a disease in which a compaction is diagnosed in the tissues of an organ. The main sign of this pathology is the presence of a dense, palpable node that has clear boundaries from healthy tissue.
Can it be completely cured?
Thyroid hormones inhibit the production of thyroid hormones and their effects become apparent after approximately 2-4 weeks of use. Commonly used beta blocker supplements, such as those, do not lower thyroid hormone levels on their own but help with some symptoms, such as hand tremors or the sensation of a rapid heartbeat. During treatment, the doctor monitors the effectiveness of the therapy using clinical assessment and thyroid hormone levels and adjusts the dose accordingly. Possible side effects with thyroiditis. If you notice any warning symptoms that may be related to starting treatment, you should tell your doctor as soon as possible. For milder complications, it is enough to change the medicine or its dose. In some very rare cases, you may need to stop thyroid therapy. A particularly dangerous, but fortunately extremely rare complication of agranulocytosis can be, that is, a significant decrease in the number of neutrophils in the serum due to reversible damage to the bone marrow toxicity that persists after discontinuation of the drug, however, this requires strict medical supervision. This is a very dangerous condition, because the body’s resistance to infection has deteriorated greatly at this time. This is why, in case of fever, weakness, sore throat, the patient should immediately stop taking the medicine and urgently inform the clinic or hospital to check the morphology with a smear. If the neutrophil count does not decrease, immediate treatment should be taken immediately. If agranulocytosis is confirmed, this group of drugs can no longer be used in the future. treatment with radioactive iodine. Oral one-time use of radioactive iodine is aimed at slow, irreversible damage to the thyroid gland, which actively takes iodine from the blood. The effect of radioactive iodine develops several months after therapy. The development of persistent hypothyroidism cannot be considered a complication, but an effect effective treatment. This form of therapy should not be used in pregnant or breastfeeding women. In addition, the treating person should not contact small children or pregnant women for one week. Finally, within at least Women should not plan pregnancy for 6 months after therapy. Surgical treatment. This form of therapy is absolutely indicated in cases of suspected or diagnosed thyroid cancer, including coexistence with hyperthyroidism. Besides, surgical treatment suggested in patients with a large tracheal tendon. Thyroid dysfunction occurs after thyroid surgery, requiring continued treatment with thyroxine. Unfortunately, during surgery you should be aware of the possibility of complications, which should be discussed with your consultant.
- Pharmacological treatment with antithyroid drugs.
- Each doctor individually sets the initial dose of the medicine.
Hypothyroidism is a disease that is accompanied by decreased thyroid function and insufficient production of thyroid hormones. Here the opposite reaction occurs - body weight increases, clarity of speech is impaired, the skin acquires a yellow tint and begins to peel off. Muscle pain, swelling of the eyelids and limbs may occur.
A gland cyst is a cavity formed in the tissues of an organ, inside of which there is fluid. If it is small in size, then there are no symptoms indicating its presence, but when the cyst suppurates, pain appears in the anterior neck.
Thyroiditis is an inflammatory disease caused by bacteria and viruses. The patient may complain of an increase in the size of the thyroid gland, pain in the organ area and headaches.
Causes of thyroiditis
The causes of goiter are divided depending on its type.
Endemic diffuse goiter:
- insufficient presence of iodine in the body, which leads to dysfunction of the organ
- polluted environment, in which toxic substances enter the body and slow down the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Nodular goiter:
- disruption of the process of tissue cell division as a result of exposure to radiation, toxic substances, or genetic predisposition.
Toxic goiter:
- the presence in the blood of antibodies that help stimulate the thyroid gland.
How to diagnose pathology
Ultrasound is considered one of the simplest and most accessible methods for diagnosing the condition of the thyroid gland. This procedure is prescribed by an endocrinologist if he detects any changes in the organ during palpation and external examination.
Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland evaluates:
- size and volume of the organ
- density and structure
- in the presence of formations (cysts, tumors) – their shape, nature and size
- the condition of the lymph nodes in the neck, which can change with gland cancer.
No preparation is required for this study. How much a thyroid ultrasound costs will depend on the city and clinic where the procedure will be performed (on average from 400 to 1200 rubles).
Interpretation of the study for pathologies
Diffuse toxic goiter:
- the thyroid gland is enlarged in volume (more than 25 ml in men, more than 19 ml in women)
- the structure of the gland is normal.
Nodular goiter:
- a limited focus of increased density is clearly visible.
Thyroiditis:
- swelling and slight increase in organ volume
- Limited cavities with fluid (pus) inside may be observed.
Tumors:
- the presence of foci of compaction limited to neighboring tissues (adenoma) or growing in them (cancer).
Cyst:
- the presence of a round cavity with clear contours and liquid inside.
Goiter treatment
The main method of treating people with this pathology is therapy, which is based on taking hormones. For this purpose, the drug L-thyroxine is prescribed, the dosage of which is selected by the doctor, based on the results of ultrasound and additional tests.
At this time it is necessary constant monitoring the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone. If the dosage is selected correctly, it should not exceed 1 IU/l. In older people, close monitoring of heart function is required during treatment.
If pain and increased heart rate occur, you should immediately stop taking the drug. The duration of treatment for the disease ranges from 8 months to 2 years, depending on the effect of the drug and the stage of the disease.
Disease prevention
The main preventive measure to prevent the disease is taking iodine supplements. Its average daily dosage is:
- children from 12 months to 2 years – 50 mcg
- from 2 years to 6 – 100 mcg
- from 6 years – up to 12 – 150 mcg
- from 12 years old and adults – 200 mcg.
If the thyroid gland is enlarged, then it can be assumed that there is a malfunction in the functioning of the endocrine system. The presence of this pathology can be detected using an ultrasound examination of the organ. If the disease is confirmed, treatment is prescribed, the duration of which is at least 8 months.
Watch the video about problems with the thyroid gland and ways to solve them.









